Advantages of open-source technology offer a compelling alternative to proprietary software, promising cost savings, enhanced flexibility, and robust community support. This exploration delves into the multifaceted benefits, examining how open-source solutions empower users with control, transparency, and collaborative innovation.
From the significant cost reductions achieved through readily available, often free, software licenses to the unparalleled customization options afforded by access to the source code, open-source presents a compelling proposition for individuals and organizations alike. The vibrant communities surrounding these projects provide invaluable support, ensuring rapid problem-solving and continuous improvement, ultimately fostering a more secure and reliable technological landscape.
Cost-Effectiveness
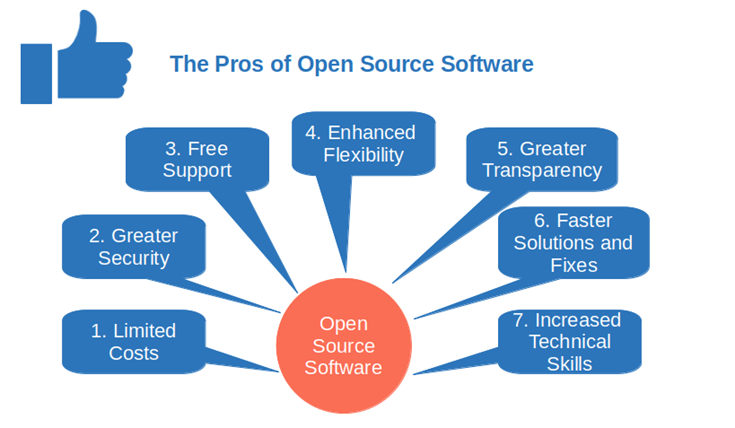
Open-source technology offers significant financial advantages over proprietary software, impacting both initial investment and long-term maintenance costs. The core principle lies in the elimination or reduction of licensing fees and the availability of extensive community support, resulting in substantial savings for individuals and organizations alike.
The financial benefits of open-source software are multifaceted. Unlike proprietary software, which often demands significant upfront licensing costs and recurring subscription fees, open-source alternatives frequently come with little to no cost associated with their use. This immediately reduces the financial burden, especially for smaller organizations or individual developers with limited budgets. Furthermore, the cost savings extend beyond initial acquisition; the ongoing maintenance and support are also significantly cheaper, thanks to the large and active communities surrounding most popular open-source projects.
Examples of Open-Source Projects with Low or No Licensing Costs, Advantages of open-source technology
Many widely used open-source projects exemplify the cost-effectiveness of this approach. For instance, Linux, a popular operating system, is freely available for download and use, eliminating the need for expensive licenses associated with proprietary operating systems like Windows or macOS. Similarly, the Apache web server, a cornerstone of the internet’s infrastructure, is open-source and free to use, offering a robust and reliable alternative to commercial web servers. Other examples include MySQL (a relational database management system), PostgreSQL (another powerful open-source database), and countless others spanning various applications and needs. These examples demonstrate that high-quality, reliable software can be accessed without significant upfront investment.
Long-Term Cost Savings Associated with Community Support and Readily Available Updates
The long-term cost advantages of open-source software are equally compelling. The vibrant communities surrounding these projects provide a wealth of readily available support, including online forums, documentation, and user-contributed solutions. This readily available assistance reduces the need for expensive commercial support contracts, a significant cost factor for proprietary software. Furthermore, open-source projects typically benefit from frequent updates and security patches, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and associated costs associated with system breaches or downtime. The collective effort of the community ensures the software remains current, secure, and efficient, reducing the need for expensive maintenance contracts or specialized IT personnel solely focused on patching and updates. This collaborative model translates directly into long-term cost savings, making open-source a fiscally responsible choice.
Transparency and Security
Open-source software’s inherent transparency significantly enhances its security posture. Unlike proprietary software where the codebase remains hidden, open-source projects encourage community scrutiny, leading to faster identification and resolution of vulnerabilities. This collaborative approach fosters a more secure ecosystem for everyone.
The open nature of the source code allows independent security audits and penetration testing by experts worldwide. This distributed security review process acts as a powerful defense mechanism, identifying potential weaknesses that might otherwise remain undetected in closed-source systems. Furthermore, the ability for developers to review the codebase directly allows them to understand how the software works and to anticipate potential issues. This proactive approach is a key differentiator in achieving high levels of security.
Examples of Secure Open-Source Projects
Many prominent open-source projects demonstrate robust security practices. These projects often employ rigorous testing methodologies, vulnerability disclosure programs, and active community involvement in security maintenance. For instance, the Linux kernel, a cornerstone of many operating systems, benefits from a large and dedicated community constantly scrutinizing its code. Similarly, projects like OpenSSL, responsible for securing internet communications, have established comprehensive security procedures and are subject to constant review. These projects highlight the effectiveness of open-source collaboration in achieving and maintaining high security standards. The widespread adoption and continuous improvement of these projects are testament to the efficacy of the open-source approach.
Identifying and Addressing Vulnerabilities in Open-Source Software
The process of identifying and addressing vulnerabilities typically begins with security researchers or developers discovering a weakness. This discovery might be through manual code review, automated security scanning tools, or reports from users encountering unusual behavior. Once a vulnerability is identified, it’s usually reported to the project maintainers through established channels, often a dedicated vulnerability disclosure program. This program Artikels the process for responsible disclosure, ensuring that the vulnerability is addressed without causing undue harm. The project maintainers then assess the vulnerability’s severity, develop a patch, and release it to the community. This patch is then integrated into subsequent releases, ensuring that users are protected against the vulnerability. The speed and transparency of this process are significant advantages of open-source development. This collaborative approach allows for swift responses and prevents widespread exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Innovation and Advancement
Open-source software development’s collaborative nature is a powerful engine for innovation. The inherent transparency and accessibility of the source code allow for a multitude of developers to contribute, review, and improve upon existing projects, leading to faster development cycles and more robust solutions than would be possible in a closed-source environment. This collaborative process fosters a diverse range of perspectives and expertise, ultimately leading to more creative and effective outcomes.
The open and shared nature of development significantly accelerates progress. Multiple developers working concurrently on different aspects of a project, along with a vast community providing feedback and bug fixes, results in a much more rapid pace of innovation compared to traditional, proprietary software development models. This speed is particularly crucial in rapidly evolving technological landscapes, where swift adaptation is key to competitiveness.
Examples of Open-Source Driven Advancements
Open-source technologies have been instrumental in driving advancements across numerous sectors. The Linux operating system, for example, underpins a significant portion of the world’s servers and embedded systems, demonstrating its reliability and scalability. Its open nature has allowed for countless modifications and adaptations, fueling innovation in areas like cloud computing and high-performance computing. Similarly, the Apache web server, another cornerstone of the internet’s infrastructure, has benefited from continuous community contributions, leading to its widespread adoption and ongoing refinement. In the field of artificial intelligence, TensorFlow, an open-source machine learning library, has democratized access to advanced AI tools, empowering researchers and developers worldwide to push the boundaries of the field. The rapid development and widespread adoption of these technologies showcase the power of open-source collaboration.
Rapid Development and Feature Additions
The speed of development and the frequency of feature additions in open-source projects are often significantly faster than their closed-source counterparts. This is a direct consequence of the collaborative nature of the development process. A large pool of developers, each with their own expertise and motivations, contributes to a continuous cycle of improvement. Bug fixes are often implemented within days or even hours, new features are added regularly based on community feedback and identified needs, and the overall functionality of the software is constantly enhanced. This rapid iteration allows open-source projects to adapt quickly to changing requirements and technological advancements, maintaining their relevance and competitiveness. For instance, the rapid evolution of web browsers like Firefox, built on open-source principles, demonstrates this continuous improvement cycle. New features, security updates, and performance enhancements are regularly integrated, reflecting the dynamic nature of open-source development.
Interoperability and Integration: Advantages Of Open-source Technology
Open-source technology fosters a collaborative environment where different systems can communicate and share data seamlessly. This interoperability, driven by open standards, is a significant advantage, leading to increased efficiency and flexibility in software development and deployment. The ability to integrate various open-source components allows for the creation of customized solutions tailored to specific needs, avoiding the limitations often imposed by proprietary systems.
Open standards, the cornerstone of open-source interoperability, define common protocols and formats for data exchange. This ensures that different applications, developed by independent teams or organizations, can interact effectively without requiring custom interfaces or complex adapters. This contrasts sharply with proprietary systems, which often necessitate costly and time-consuming integration efforts. The adoption of open standards promotes a more efficient and cost-effective ecosystem where components are readily interchangeable.
Seamless Integration Examples
Several successful examples showcase the power of seamless integration within open-source ecosystems. For instance, a content management system (CMS) like WordPress can be readily integrated with numerous open-source plugins and extensions, expanding its functionality without requiring specialized coding or proprietary solutions. Similarly, a business might integrate an open-source CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system with an open-source ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, creating a unified platform for managing customer interactions and business processes. The use of standardized APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) facilitates this type of integration, allowing different systems to exchange data and functionality smoothly. Another example would be the integration of open-source databases like PostgreSQL or MySQL with various programming languages and frameworks. This interoperability allows developers to choose the most suitable tools for their specific project, without being constrained by vendor-specific limitations.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-in
The freedom from vendor lock-in is a compelling benefit of open-source software. Proprietary software often ties users to a single vendor, limiting their options for customization, upgrades, and migration. If a vendor ceases operations or changes its pricing structure, businesses using their software face significant disruption. Open-source software, in contrast, offers freedom from such constraints. Users can choose from a wide range of vendors or even self-host their applications, maintaining control over their data and software infrastructure. This flexibility minimizes risks associated with vendor dependence, allowing for greater agility and adaptability to changing business needs. For example, a company using a proprietary CRM system might find it difficult and costly to switch to a different system if they are unhappy with the vendor’s service or pricing. However, if they were using an open-source CRM, migrating to another open-source solution would be significantly easier and more cost-effective.
Scalability and Reliability

Open-source platforms offer significant advantages in terms of scalability and reliability, stemming from their inherent design and the collaborative nature of their development. This translates to cost-effective solutions that can adapt to changing demands and maintain operational stability over time, even under significant pressure.
The scalability and reliability of open-source solutions are largely due to their modular architecture and the extensive testing they undergo. Many open-source projects are built using a modular design, allowing for easy addition or removal of components as needed. This flexibility makes it relatively simple to scale the system up or down depending on the current workload. Furthermore, the large, active communities surrounding these projects contribute significantly to rigorous testing and bug fixing, leading to enhanced reliability and stability. This community-driven approach ensures that potential issues are identified and addressed quickly, reducing downtime and improving overall system performance.
Community-Driven Testing and Enhancement
The open nature of open-source projects facilitates a robust testing process that surpasses what’s typically possible in proprietary software. Thousands, sometimes millions, of users worldwide contribute to identifying bugs, suggesting improvements, and testing new features. This widespread testing across diverse environments (hardware, operating systems, network configurations) reveals weaknesses and edge cases that might otherwise go unnoticed in a closed development environment. For example, the Linux kernel, the backbone of many servers and embedded systems, benefits immensely from this community-driven approach. The constant scrutiny and contributions from developers worldwide have resulted in a remarkably stable and reliable operating system kernel. The rapid identification and resolution of security vulnerabilities are a direct result of this collaborative testing and development model. Similarly, the Apache web server, another cornerstone of the internet’s infrastructure, has achieved exceptional reliability through years of community involvement and rigorous testing.
Scalability to Meet Growing Demands
Open-source solutions are frequently designed with scalability in mind. Many popular open-source databases, such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, are capable of handling massive datasets and high transaction volumes. Their scalability is often achieved through techniques like horizontal scaling (adding more servers to distribute the workload) and sharding (partitioning the database across multiple servers). This allows organizations to seamlessly accommodate growth without needing to migrate to a completely new system. For instance, a small business using an open-source e-commerce platform can easily scale its infrastructure as its customer base and sales volume increase, simply by adding more servers or adjusting database configurations. This flexibility and scalability represent a significant cost advantage compared to proprietary solutions, which may require costly upgrades or complete system replacements to handle growing demands. This scalability is further enhanced by the availability of readily available, well-documented APIs and tools that facilitate integration with other systems and services.
Access to Source Code and Customization Options
Open-source software’s greatest strength lies in its accessibility. Unlike proprietary software where the inner workings remain hidden, open-source grants users direct access to the source code, unlocking a world of possibilities beyond simple usage. This transparency fosters a deeper understanding of the software’s functionality and empowers users to tailor it to their specific needs.
Direct access to the source code allows for a level of control and customization unavailable with closed-source alternatives. This granular control extends from minor tweaks to significant modifications, enabling users to address specific issues, enhance existing features, or even add entirely new functionalities. The ability to understand how the software operates at its core facilitates efficient troubleshooting and problem-solving, allowing for faster resolution of unexpected issues.
Benefits of Source Code Access
Having direct access to the source code provides several key advantages. Firstly, it allows for thorough debugging and identification of the root cause of problems. Secondly, it enables users to adapt the software to unique environments or workflows that might not be adequately addressed by the standard version. Finally, it facilitates the creation of custom features or integrations with other systems, significantly enhancing the software’s value and usefulness. Consider a scenario where a small business uses open-source accounting software. They might discover the need for a specific report not included in the standard package. With access to the source code, their in-house developers (or a hired consultant) can add this custom report, perfectly tailored to their business’s reporting requirements, without relying on the original developers or waiting for updates. This significantly reduces reliance on external support and speeds up the implementation of necessary changes.
Customization for Specific Use Cases
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario involving a hospital using open-source medical imaging software. The standard software might offer excellent image processing capabilities, but the hospital needs a specific feature for analyzing a newly developed type of medical scan. Because the software is open-source, the hospital’s IT department or a specialized team can modify the source code to integrate the necessary algorithms for analyzing this new scan type. This customized solution directly addresses the hospital’s unique needs, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, and avoids the potential delays and costs associated with waiting for a commercial vendor to develop and release the feature. This tailored approach demonstrates the significant advantage of open-source software in adaptable and dynamic environments like healthcare.
In conclusion, the advantages of open-source technology extend far beyond mere cost savings. The collaborative nature of open-source development fosters innovation, transparency, and security, creating a robust and adaptable ecosystem that benefits both users and developers. Embracing open-source represents a commitment to shared knowledge, community-driven progress, and a future where technology is accessible, adaptable, and secure.
Open-source technology fosters collaboration and innovation, leading to faster development cycles and cost savings. This is particularly relevant in rapidly evolving fields like augmented reality, where the accessibility of tools is crucial. For instance, exploring the capabilities of Augmented reality (AR) AI tools becomes significantly easier with open-source frameworks, further accelerating advancements and broadening accessibility to this technology.
Ultimately, the transparency and shared development inherent in open source amplify the benefits for everyone involved.
Open-source technology offers numerous benefits, including community-driven development and cost-effectiveness. These advantages are particularly relevant in the context of managing and processing information, as seen in the increasing reliance on Big Data and cloud storage. The flexibility and transparency of open-source solutions make them well-suited for the complex challenges of big data analysis, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency and security of the entire system.
